Services

Services
Comprehensive Eye Exam
A comprehensive eye examination extends beyond the assessment of corrective lenses, encompassing a thorough evaluation of your ocular health. Here is a compilation of typical components frequently encompassed within your eye examination.
- Patient History: The eye doctor will begin by gathering information about your medical history, including any current eye conditions, past eye problems, family history of eye diseases, and general health status.
- Visual Acuity Test: This test involves reading letters or symbols on an eye chart from a specific distance to determine your visual clarity and assess if you need corrective lenses.

- Refraction Test: This test helps determine your precise eyeglasses or contact lens prescription by assessing how different lenses affect your vision.
- Eye Muscle Movements: The doctor checks the coordination and movement of your eye muscles by asking you to follow an object with your eyes.
- Pupil Assessment: The size, shape, and reaction of your pupils to light are examined to assess the health of the neurological pathways and overall eye function.
- Peripheral Vision Test (Visual Field Test): This test assesses your side vision and detects any blind spots or abnormalities that could indicate eye diseases.
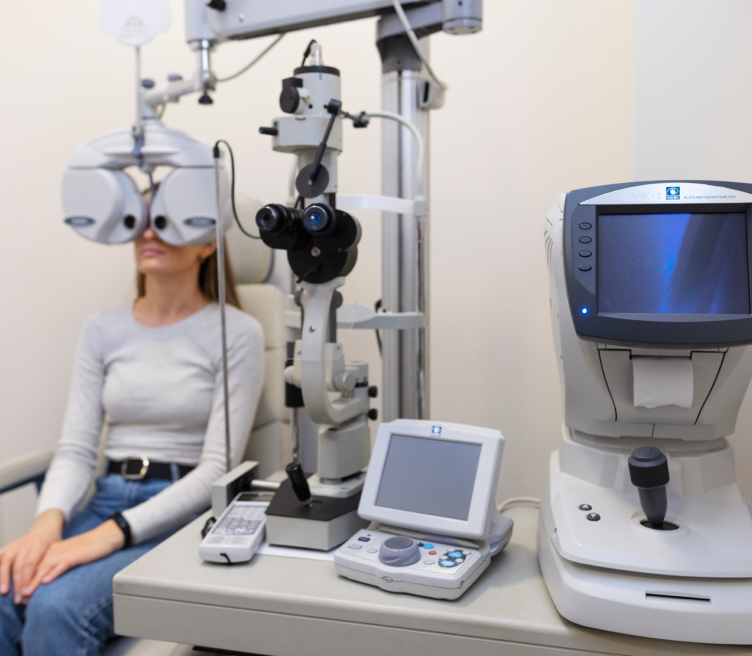
- Intraocular Pressure Measurement: This test measures the pressure inside the eye to screen for glaucoma. It’s typically done using a tonometer.
- Slit Lamp Examination: A biomicroscope is used to examine the front of your eye, including the cornea, iris, lens, and anterior chamber, for any abnormalities or signs of disease.
- Dilated Fundus Examination: The doctor uses eye drops to dilate your pupils and examines the retina, optic nerve, blood vessels, and other structures at the back of the eye.
